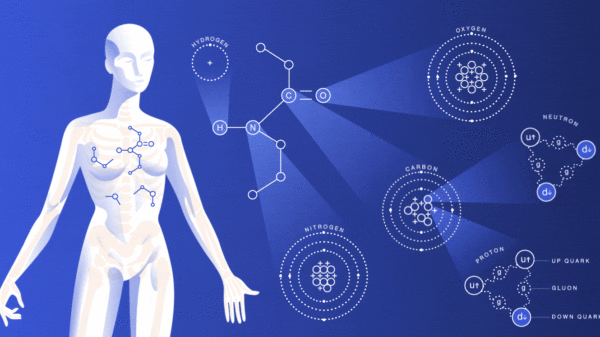
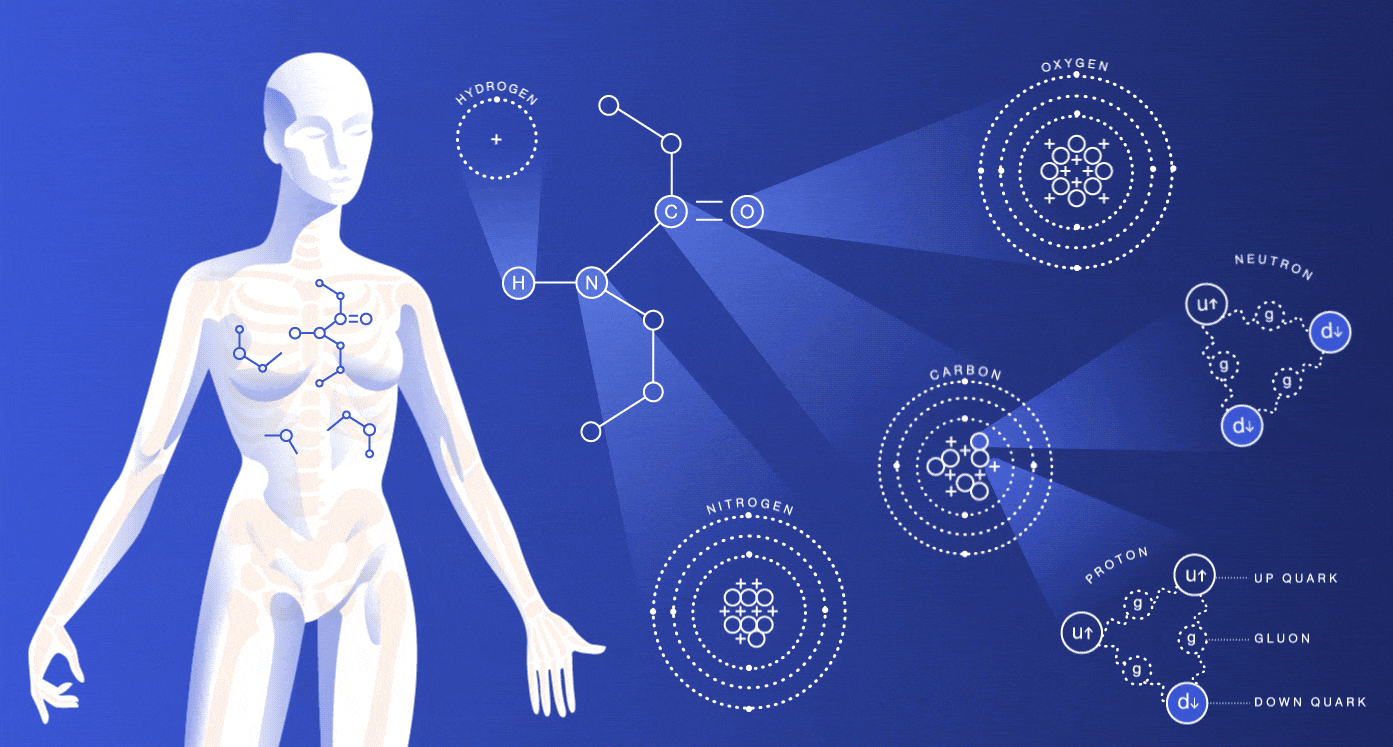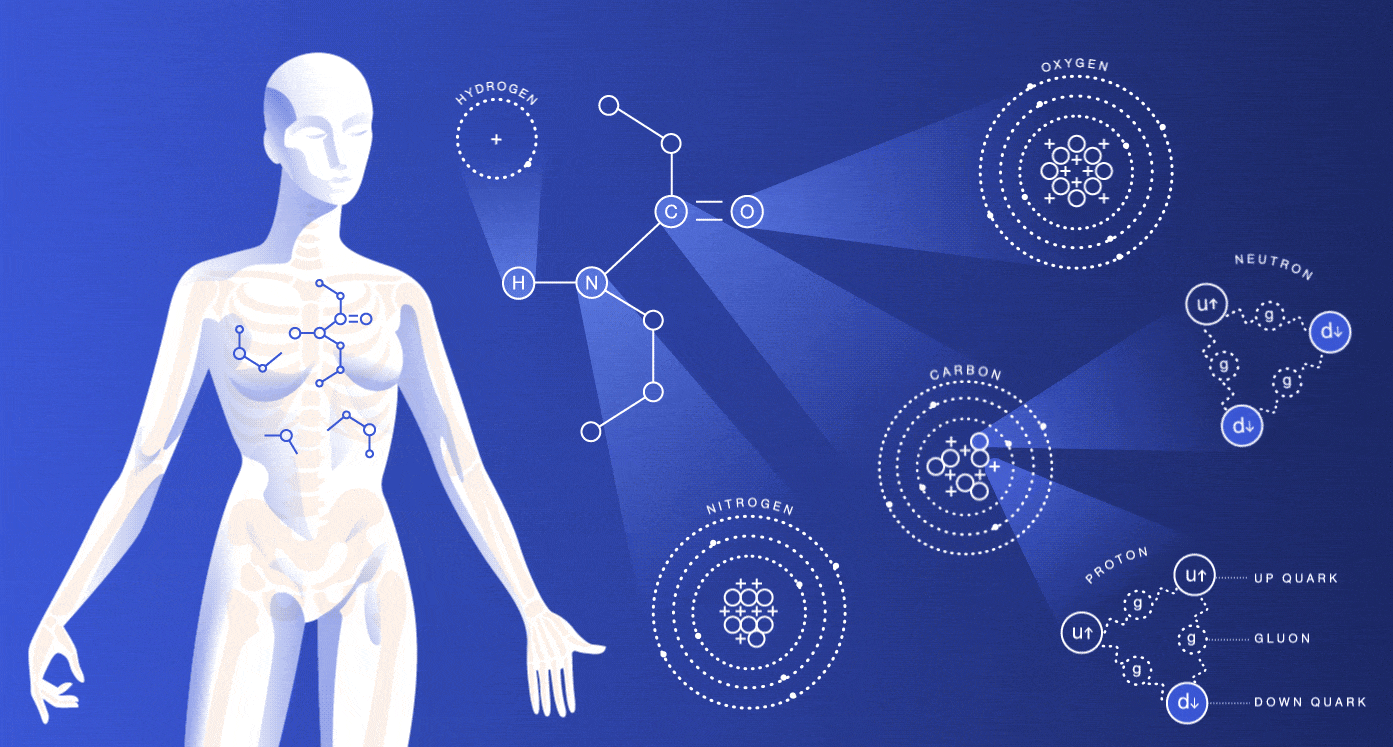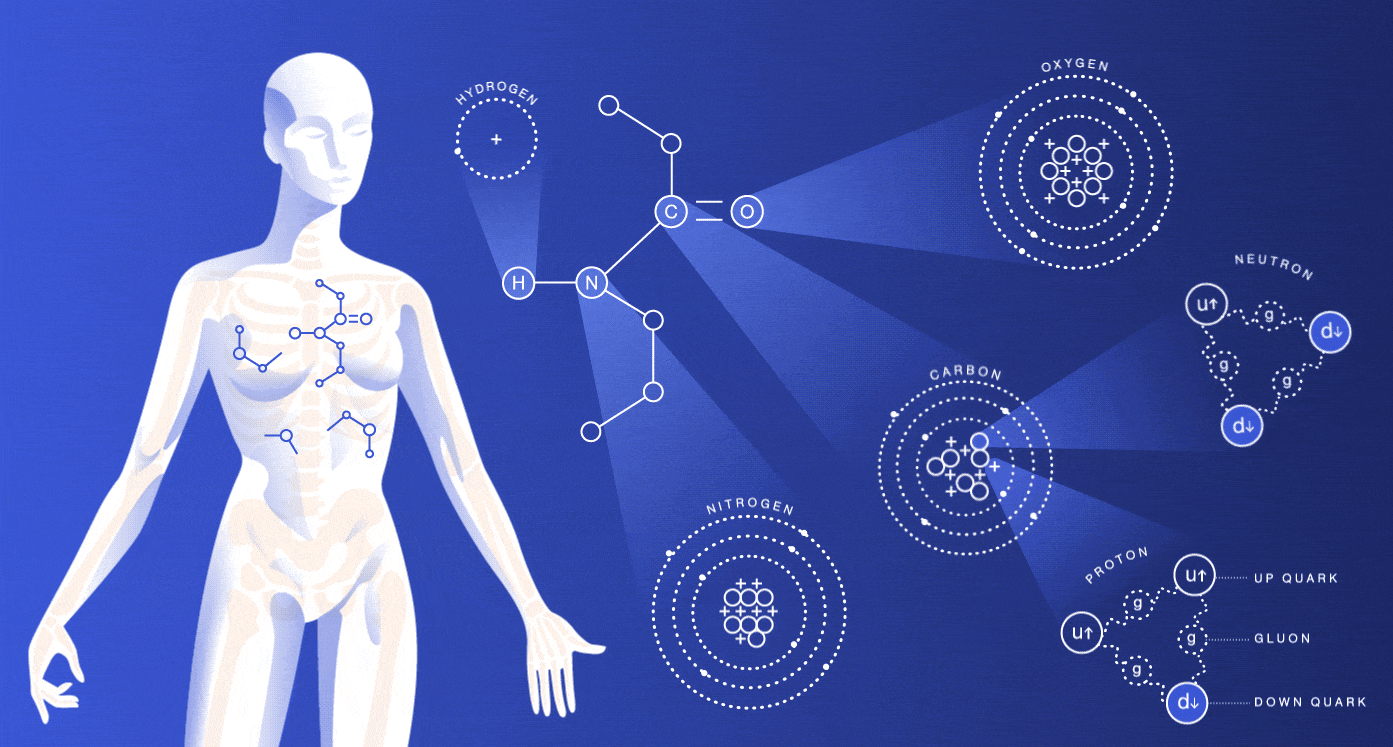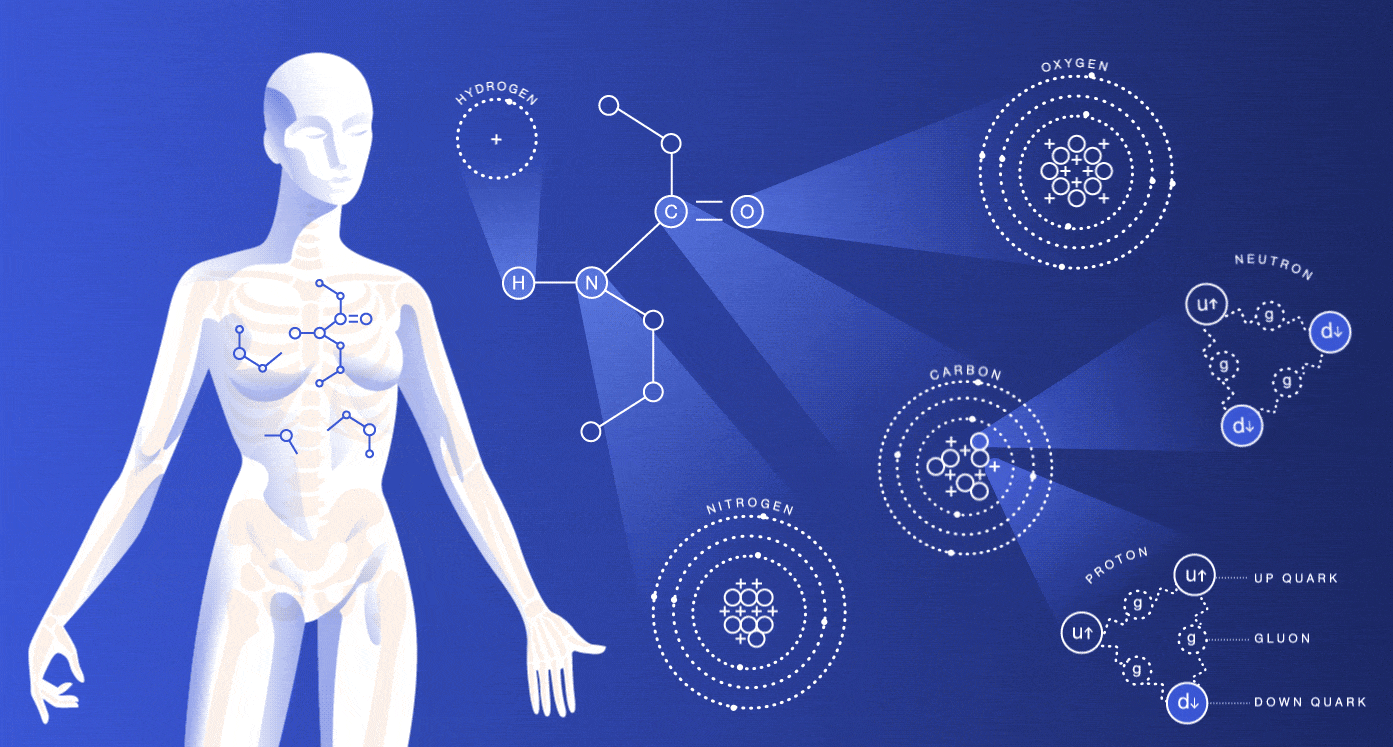
A human body is composed of different elements with various functions. As we all know that, our body is made up of water by combining hydrogen and oxygen in a fixed ratio. Around 60 chemicals are found in our body but still, the majority of functions of those elements are unknown. Not all the elements which are present in our body are essential, but some elements are important for the sustain of our life.
Our body has four major elements which constitute 96% of the mass of the human body. Those four elements are carbon (C), oxygen (O), hydrogen (H) and nitrogen (N). The next six elements important for the human body are calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, iron, sulphur and sodium. Each of them plays different roles and here are some detailed explanations of their respective functions and importance.
Functions of elements in our body
Oxygen
In the human body oxygen is the most abundant element. Oxygen when combined with hydrogen forms water which is the primary solvent found in the body that regulates temperature and osmotic pressure in the human body. Another essential part of oxygen is that it acts as an oxidizing agent and electron acceptor. In our body, protein, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids are organic molecules.
- Oxygen is present in these molecules because the role in aerobic cellular respiration is inevitable.
- In blood haemoglobin binds oxygen from inhaled air.
- Mitochondria in cells use oxygen to produce the energy molecule adenosine triphosphate or ATP.
Carbon
The atomic number of carbon is 6 and composed of 18% of the body weight. It is not found in pure form but as compounds. For proteins like carbohydrates and fats, carbon plays as a building block. Carbon is also found as CO2. The inhaled air in the body is about 20% oxygen, and that of exhaled air is a lot less oxygen and more carbon dioxide. When we breathe carbon is expelled from carbon dioxide as a waste product,
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is found in organic molecules in the form of water. Water is formed when hydrogen combines with oxygen. It acts as a proton or positive ion in the reactions. Hydration of cells is due to hydrogen, and also it eliminates hydrogen. It also plays a vital role in the energy production in our bodies.
Nitrogen
The air we breathe comprises 78% of nitrogen. Nitrogen is obtained from the foods like meat, and it is the main component of amino acids and urea. The nucleic acid DNA makes up your genes, and RNA is involved in protein synthesis, which needs nitrogen.
- It helps in digestion and growth.
- Necessary for the foetus growth
Calcium
It is one of the essential elements for our bones and teeth. In addition, calcium is a crucial ion used in muscle contraction and protein regulation. The sources of this element are curd, milk and cheese etc. For calcium deficiency, calcium phosphate is used in the medical field.
- It is vital in preventing the excessive flow of blood.
- It plays an essential role in skin repair and self-replenishing.
Phosphorus, potassium and Sulphur
- Phosphorus is found in nucleic acid and energy molecules, such as ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
- For the regulation of heartbeat and the conduction of nerve signals, potassium has a great role.
- Sulphur is found in biotin, methionine, thiamine, and cysteine.
Summary
The human body is composed of many elements which have vital roles and functions to perform. Carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen and oxygen are the main four elements present in the body. Each of them performs different functions, which are inevitable for the growth and development.